The last major ice age began in the Alps at the end of quaternaire.About 70 000 years ago, begins the Würm glaciation, which reaches its maximum 25 000 years ago.
At that time, ice covered all the Alpine valleys. Indeed, the Mont Blanc glacier covered the whole Arve valley to Geneva, the Rhone Glacier in Switzerland reached then the gates of the city of Lyon (about 15 km, at the current airport) . The Rhone glacier was joined by some parts of the glacier Isère (Grenoble).
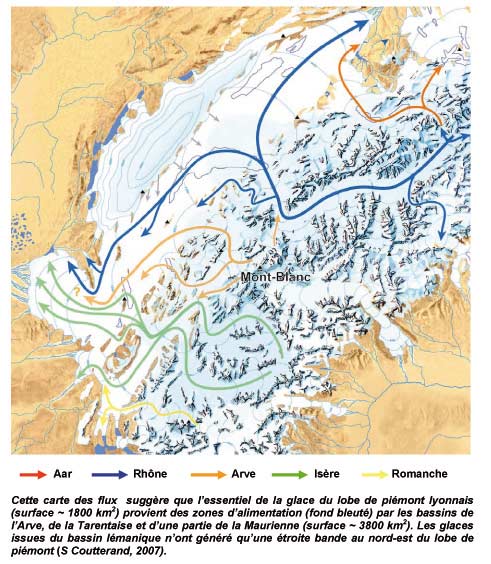
Mont Blanc valley and the main glaciers during the Würm (Geo- Alpes, 2010)
This extreme development of Glaciers, particularly in France and Switzerland explained in part by the topography of this area of the Alps. The slopes are less steep and glacial cirqueswider. Ice has no problem extending into the valleys, forming a thick and solid layer.
In the "Research on the Ice Age and the former extension of glaciers of Mont Blanc from the Alps to the Jura" Charles Martin explains that during this period, temperatures in Geneva should have decreased by 4 or 5 ° C (from 10 to 5 degrees), this way and due to the altitudinal gradient (the air temperature decreases by 1 ° C every 188 meters) the eternal snow line being lowered then 2700 m to 1955 meters. The bottom of the glacier also be lowered by 750 meters and therefore reach the Swiss plain. This plus the fact that the glacier of Mont Blanc (glacier of the Arve) is located in an area large circuses explains the fact that the glacier have been able to reach the town of Geneva from Chamonix.
the ice age left its mark in the Alps and in particular in France in the Alps in the north. Glaciers are large "erosion machines" and deep valleys post coolers are formed after the retreat of the ice like the Grésivaudan valley (Albertville, Grenoble) which now forms a deep U-shaped valley.

Grésivaudan valley from le Touvet ( Wikipedia, 2011)
The first result of glaciation of such importance is the decline in sea level (120 meters lower than today during the Würm). This lowering of sea level causes a decrease in the surface of the continental shelf (richest lifezone). Furthermore, the thermal gradient becomes higher, this leads for each species to a trophic zone which decreases thus increasing the competition between species.
Phase of ice to survive, a species subject to too much cold for them, should descend to the plains and find new ecologic shelters. They must do so especially since they are sensitive to cold, or survive in smaller populations and sometimes less dense in areas of refuge less affected by cold.
During the last ice age, it does not appear to have been much loss of overall species on the planet, but for species with low dispersal ability, the cold has caused the local extinction of many populations in metapopulations then existing, with the corollary reduction of genetic diversity in some groups, these effects "negative" for biodiversity can be mitigated by the dewatering of the continental shelves helped by lower sea levels. Thus there were new areas that have reconnected habitats almost disjoint (set out for birds and marine mammals and some species) during interglacial phases (eg the current France was reconnected to the current United Kingdom during the last ice age, allowing large mammals (including mammoths) to move from one area to another across the current floor of the Channel and the Strait of the Pas-de-Calais. the genetic consequences of climatic oscillations, and glaciations in particular, are important. (wikipedia, 2011)
The late glaciation period has deeply shaped the Alps as we know it today.
Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire